top of page
Formula

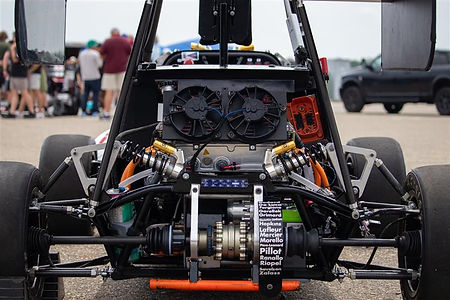
Our team combines years of knowledge from formerly building combustion race cars in building electric race cars. Our years of mechanical development let us tackle these new technologies head-on while maintaining a solid racing platform. We strive to push Concordia engineering students to become top-notch, relevant future employees in an ever-changing job market. Here at Concordia Formula Racing, we don't just make race cars go fast, we create the race car of the future.
Visit the Concordia Formula Racing Website:




bottom of page
